Awesome Tips About What Are The 5 Stages Of Simulation

Unveiling the Reality Within
Ever wondered if what you see, feel, and experience is truly "real"? The question of whether we're living in a simulation has captivated philosophers, scientists, and sci-fi enthusiasts alike. While we can't definitively answer that head-scratcher just yet, delving into the stages of simulation can offer some intriguing food for thought. And hey, even if we aren't in a simulation, understanding these stages can still help us better grasp how complex systems work in general. Think of it like this: its a deep dive into models, approximations, and the quest for perfect replication of reality, whether that reality is tangible or digital.
1. Defining "Simulation"
Before we jump into the stages, let's clarify what we mean by "simulation." We're not just talking about playing the latest Grand Theft Auto (though, that could be considered a simulation on some level). A simulation, in a broader sense, is a model or representation of a real-world system or process. It's about replicating behaviours and characteristics, and often, predicting outcomes. From weather forecasting to engineering design, simulations are everywhere.
So, when we ponder the possibility of our reality being a simulation, we're essentially asking if there's a highly advanced system capable of perfectly mimicking consciousness, physical laws, and the vastness of the universe. Heavy stuff, right? Let's move on to the stages. This topic is often debated by many scientists, but with limitations.
The concept often pops up in philosophical discussions and science fiction. It challenges our fundamental understanding of existence and reality. While we don't have concrete proof of a grand simulation, the advancements in technology and our growing ability to model complex systems make the idea fascinating to consider.
These simulations can take many forms. It includes computer models that are used in scientific research, financial analysis, or the design of new products. It also encompasses virtual reality experiences that immerse us in entirely different worlds. All these different kinds of simulations are trying to accomplish one thing, recreating elements of reality in a way that allows us to study, explore, or even alter them.

Stages Of A Simulation Study. Download Scientific Diagram
Stage 1
2. The Blueprint of a Simulated World
Every grand project starts with an idea, right? Think of a team of developers huddled around a whiteboard, scribbling down concepts, algorithms, and initial parameters. This is where the essence of the simulation is born. The goal of conceptualization is to identify what you aim to simulate, what level of fidelity is required, and what resources you'll need to pull it off. If the aim is simulating a whole universe, for example, the plan would look very complex and would consume a considerable amount of time.
At this stage, the boundaries are set. What aspects of reality will be included? What can be simplified or ignored? If you are building a model of the economy, for instance, the planners might need to decide if things like irrational consumer behaviour, or geopolitical dynamics should be included in the simulation. Those decisions are crucial in determining the accuracy and applicability of the simulation.
Resource allocation is also vital. How much computational power will be required? What programming languages and software frameworks will be used? What kind of expertise will the team need? These early considerations shape the entire simulation process.
This preliminary phase sets the foundation. It is like laying the first brick in a virtual structure that could potentially reshape our understanding of reality itself. This stage requires a mix of imagination, strategic thinking, and technical expertise.
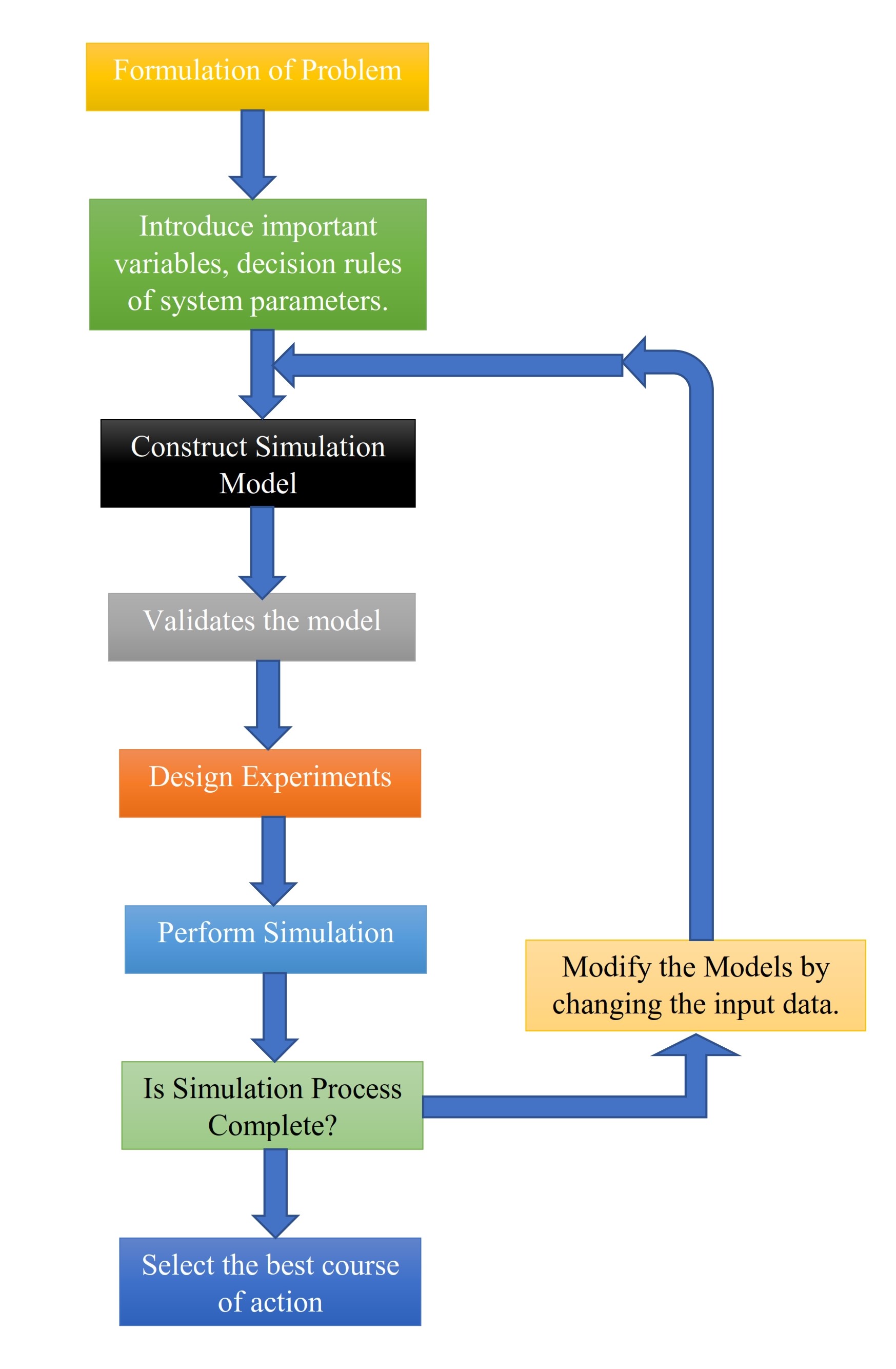
Stage 2
3. Bringing the Digital World to Life (Line by Line)
This is where the rubber meets the road (or, rather, the fingers meet the keyboard). The conceptual blueprint now takes shape in lines of code, intricate algorithms, and carefully designed data structures. This stage involves the actual creation of the simulation environment, including the rules that govern it and the entities that inhabit it. Think of it as building a digital ecosystem, one line of code at a time.
Programmers translate the initial ideas into functional code. They must ensure the code is efficient, reliable, and scalable. The choice of programming language and development tools becomes critically important. Factors such as processing speed, memory management, and cross-platform compatibility come into play.
This also involves integrating different components of the simulation, such as physics engines, AI algorithms, and rendering engines. Each component needs to work seamlessly together to create a cohesive and believable experience.
Debugging is a constant process during this stage. Errors and inconsistencies need to be identified and corrected. The development team must continuously test and refine the code to ensure it meets the design specifications.

Stage 3
4. Fine-Tuning the Simulated Reality
The simulation is built, but is it behaving correctly? This is where parameterization and calibration come in. It's like a mechanic fine-tuning an engine to achieve optimal performance. This stage involves setting the values of various parameters within the simulation to match real-world data and observations. It's about ensuring the simulation accurately reflects the system it's meant to represent. Think of it as making sure the simulated sun shines with the right intensity and the simulated apples fall at the right speed.
Parameterization involves defining the key variables that influence the simulation's behaviour. This could include things like gravity, air resistance, material properties, and economic indicators. The choice of parameters and their initial values will significantly impact the simulation's accuracy and predictive power.
Calibration is the process of adjusting these parameters to ensure the simulation matches historical data or experimental results. This is often an iterative process, where the simulation is run, the results are compared to real-world data, and the parameters are adjusted accordingly. This process can be quite tedious, and the simulation may require many adjustments before getting the parameters right.
Sensitivity analysis is often performed to understand how changes in different parameters affect the simulation's outcome. This helps identify the most critical parameters and allows for more efficient calibration. The goal is to ensure that the simulation accurately reflects the behaviour of the real-world system under a variety of conditions.

Stage 4
5. Let the Simulation Run (and Learn)
It's showtime! The simulation is ready to run, and data starts flowing. This stage involves executing the simulation under different scenarios and collecting the resulting data. It's like setting up a scientific experiment and observing the results. The aim is to gather insights, test hypotheses, and make predictions about the system being simulated. Picture rows of monitors displaying complex graphs and charts, revealing the inner workings of the simulated world.
The simulation is run multiple times, each time with different initial conditions or parameter settings. This allows for exploring a range of possible outcomes and assessing the simulation's sensitivity to different factors. These repeated runs help to see patterns which aren't otherwise easily spotted.
Data collection is a crucial aspect of this stage. Relevant data points are recorded and stored for later analysis. This might include things like temperature, pressure, population size, or market prices. The data needs to be organized and structured in a way that makes it easy to analyze and interpret.
Real-time monitoring is often employed to track the simulation's progress and identify any anomalies or unexpected behaviours. This allows for making adjustments on the fly and preventing the simulation from veering off course. Also, this step is important in the next step to refine and make accurate the data.
The Stages Of Simulation Process Phase Space (PhS) Stage (Left
Stage 5
6. Decoding the Meaning of the Simulated World
The simulation has run its course, and a mountain of data awaits. This final stage involves analyzing the collected data, interpreting the results, and drawing meaningful conclusions. It's like a detective piecing together clues to solve a mystery. The aim is to extract actionable insights from the simulation and use them to inform decisions, improve understanding, or test theories. Think of statisticians and domain experts poring over charts and graphs, searching for patterns and insights. It might require weeks or months to complete this stage.
Statistical analysis is often used to identify trends, correlations, and significant relationships within the data. This helps to understand how different factors interact with each other and influence the simulation's outcome.
Visualization techniques, such as charts, graphs, and animations, are used to communicate the results of the simulation in a clear and compelling way. This makes it easier for stakeholders to understand the findings and make informed decisions.
The results of the simulation are compared to real-world data or experimental results to validate the simulation's accuracy and predictive power. This helps to build confidence in the simulation's findings and ensure that they are relevant and reliable.