Casual Info About What Is The Maximum Voltage For Canbus

500V 600V 100kwh 150kwh High Voltage Lithium Ion Battery System With
Understanding the CAN Bus Voltage Landscape
1. What Powers Your Car's Chatter?
Ever wondered how all the electronic components in your car 'talk' to each other? It's not magic, it's CAN bus! Think of it as the car's central nervous system, carrying messages between everything from the engine control unit to the anti-lock brakes. But just like our nervous system relies on carefully regulated signals, the CAN bus relies on voltage. Specifically, understanding its maximum voltage is pretty crucial.
So, what exactly is this CAN bus thing? CAN stands for Controller Area Network, and it's a robust communication standard designed for noisy environments like, well, a car! It allows different microcontrollers and devices to communicate without needing a host computer. This makes your car more efficient and easier to diagnose. Imagine if every sensor needed its own wire back to the computer - that would be one spaghetti-like mess!
The CAN bus uses a differential signaling method, which means it transmits data over two wires: CAN High and CAN Low. The voltage difference between these two wires represents the data being transmitted. This differential method helps to reject common-mode noise, making the system more reliable even with electrical interference kicking around. Basically, it's designed to ignore the static and hear the message clearly. Clever, right?
Now, before we dive into the maximum voltage, let's be clear: We're talking about a system designed for reliability, so exceeding specifications is generally a bad idea. Think of it like feeding your pet hamster too much things might get a little chaotic. Stick to the guidelines, and your car's digital chatter will remain smooth and understandable.

Decoding the Maximum Voltage
2. How High is Too High? The Voltage Threshold.
Alright, let's get down to brass tacks. The standard maximum voltage for the CAN High line is typically around 3.5 volts. But hang on a second! This isn't a hard-and-fast, set-in-stone number that can never be exceeded. It's more of a guideline, a best-practice recommendation. There's wiggle room, and the exact maximum permissible voltage can vary slightly depending on the specific CAN transceiver and the network design. Consult the datasheet for your particular transceiver for precise values is always the best course of action. Consider it the manufacturer's recipe for success!
Why this "wiggle room?" Well, real-world conditions are messy. There might be voltage spikes, signal reflections, or other electrical gremlins trying to mess with the communication. The system needs to be robust enough to handle these transient events without crashing the whole party. So, while 3.5 volts is the typical upper limit for CAN High, the system is usually designed to tolerate brief excursions above that level. It's like giving the system a little buffer to breathe in case things get a bit hectic.
Going beyond the maximum specified voltage, even for a short period, risks damaging the CAN transceiver or other connected devices. Its like turning up the volume on your speakers way too high eventually, somethings going to blow. Potential consequences include data corruption, communication errors, and even hardware failure. Nobody wants that!
Think of it like this: the CAN bus is like a well-behaved orchestra. Each instrument (electronic component) needs to play its part at the right volume (voltage) for the music (data) to sound beautiful. If one instrument gets too loud, it throws off the whole performance. Staying within the specified voltage range ensures that everything plays in harmony.

What Is CANbus Voltage? Knowledge
The Importance of Termination
3. Why Resistors Matter
Okay, so we know about voltage levels, but what about those little resistors you often see lurking on a CAN bus network? These aren't just there for decoration; they play a crucial role in signal integrity and voltage control. Theyre strategically placed at each end of the CAN bus to prevent signal reflections, which can cause data corruption and communication errors. Think of it like putting up barriers at the end of a bowling alley to stop the ball from bouncing back and hitting you!
These termination resistors, typically around 120 ohms, absorb the signal energy at the end of the bus, preventing it from bouncing back and interfering with the ongoing communication. Without proper termination, those signal reflections can create voltage spikes and dips that exceed the acceptable range, potentially causing errors. They help maintain a clean and stable voltage level, essential for reliable communication. It's like making sure the bowling lane is smooth and even so the ball rolls straight.
Incorrect termination, such as missing resistors or using the wrong resistance value, can severely impact the voltage levels on the CAN bus and lead to intermittent communication problems. Imagine trying to have a conversation in a room full of echoes it's hard to understand what's being said! Proper termination ensures that the signal is clean and clear, allowing devices to communicate effectively.
So, next time you're tinkering with a CAN bus network, remember the humble termination resistor. It's not the flashiest component, but it's absolutely vital for maintaining signal integrity and ensuring that your car's digital chatter remains clear and understandable. They are essential pieces to the reliability puzzle!
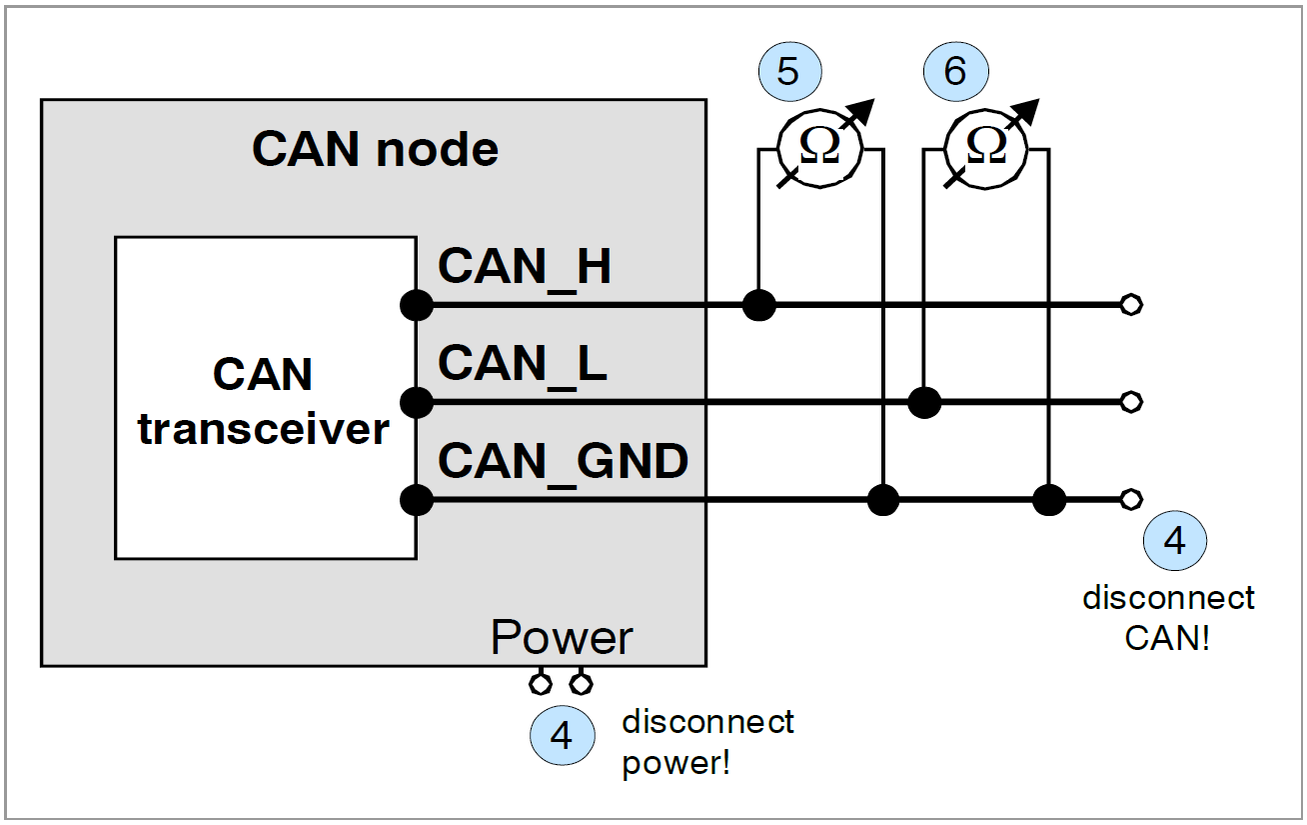
CAN Bus Troubleshooting Guide
Troubleshooting Voltage Issues
4. When Things Go Wrong
So, what happens when the CAN bus voltage isn't behaving as expected? How do you go about diagnosing the problem? Well, the first step is to grab your trusty multimeter and start measuring the voltage levels on the CAN High and CAN Low lines. A healthy CAN bus should show a differential voltage close to zero when idle and a measurable difference during data transmission.
If you see voltages outside the normal range, the next step is to start isolating the problem. Disconnect devices one by one to see if the voltage returns to normal. This can help you pinpoint the faulty device that's pulling down the voltage or causing excessive noise. It's like detective work, but with a multimeter instead of a magnifying glass!
Also, check the wiring and connections for any signs of damage or corrosion. A loose connection or a frayed wire can cause voltage drops or intermittent communication problems. Sometimes, the simplest solutions are the most effective. Its often the easiest fix!
Remember, a stable and well-behaved CAN bus voltage is essential for reliable communication. By understanding the normal voltage range and knowing how to troubleshoot voltage issues, you can keep your car's digital nervous system functioning smoothly. And that, my friend, is a good thing!

Factors Affecting CAN Bus Voltage
5. External Influences
Numerous factors can influence the CAN bus voltage, creating variations from the ideal values. Understanding these factors is crucial for diagnosing and resolving communication issues. One major factor is the power supply voltage. Fluctuations or instability in the power supply can directly impact the voltage levels on the CAN bus. Ensuring a clean and stable power source is essential for reliable communication.
Electrical noise and interference, generated by nearby motors, relays, or other electrical equipment, can also affect the CAN bus voltage. Shielded cables and proper grounding can help mitigate these effects. Think of it as building a Faraday cage around your CAN bus network to protect it from outside interference. This helps keep those pesky volts under control. It's like creating a bubble of serenity amidst the chaos of the engine bay!
The length of the CAN bus and the number of connected devices can also influence voltage levels. Longer bus lengths and more devices increase the load on the system, potentially causing voltage drops. Using appropriate cable types and ensuring proper termination are crucial for mitigating these effects. Its like planning a long road trip and making sure your car has enough fuel to reach the destination. You dont want to run out of power halfway there!
Finally, environmental factors such as temperature and humidity can also play a role. Extreme temperatures can affect the performance of electronic components, potentially altering the CAN bus voltage. Similarly, high humidity can lead to corrosion and connection problems, which can also impact voltage levels. Keeping the system clean and dry is always a good idea. A little preventative maintenance goes a long way!

Professional Wiring Of Galvanically Isolated CAN Networks
FAQs
6. Q
A: If the CAN bus voltage is too low, communication becomes unreliable. Devices might not be able to properly interpret the signals, leading to data corruption, errors, or complete communication failure. It's like trying to whisper secrets in a crowded room nobody can understand you!
7. Q
A: Yes, you can use a regular multimeter to measure CAN bus voltage, but an oscilloscope is better for visualizing the signal waveform and identifying noise or signal reflections. A multimeter will give you a general sense of the voltage levels, but an oscilloscope provides a more detailed picture of what's happening on the bus. Think of it as comparing a snapshot to a video.
8. Q
A: The specified maximum voltage for your CAN transceiver is typically found in the datasheet provided by the manufacturer. The datasheet contains detailed information about the device's electrical characteristics, including the maximum operating voltage and other important specifications. Its the bible for your transceiver.